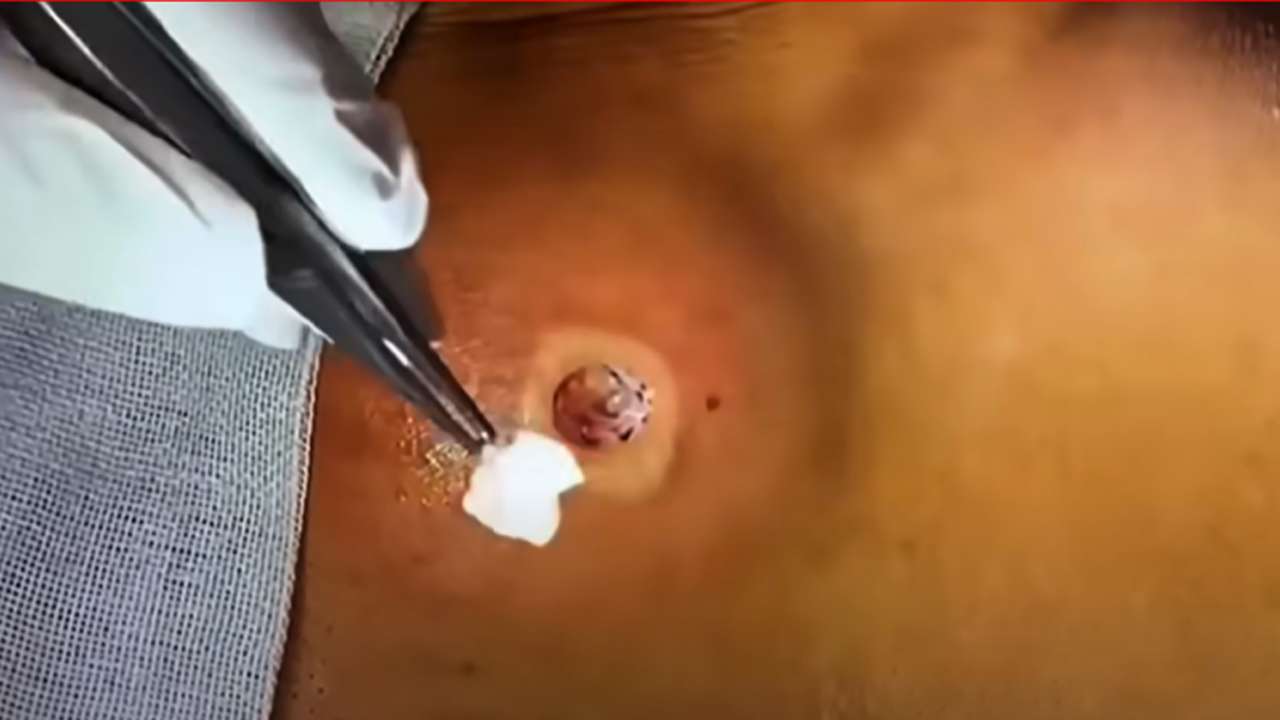
A lipoma and a cyst are two different types of lumps under the skin, and the way to deal with them varies depending on which one you have. Here’s a breakdown of what they are and how they’re treated:
🧠 Lipoma vs. Cyst: What’s the Difference?
Feature
Lipoma
Cyst (e.g., sebaceous/epidermoid)
Type
Fatty tumor (benign)
Fluid-filled sac (usually keratin or sebum)
Feel
Soft, rubbery, moves under skin
Firm or soft, may be tender
Growth
Slow-growing
Can appear quickly
Pain
Usually painless
Can be painful, especially if infected
Location
Common on arms, shoulders, back
Common on face, neck, scalp, back
🛠️ Treatment Options
🧴 1. Home Care (for Small, Uncomplicated Cysts Only)
⚠️ Home treatment is not recommended for lipomas or inflamed/infected cysts.
Warm compress: Helps reduce swelling and promote drainage (for small, non-infected cysts).
Do NOT squeeze or pop – this can cause infection or scarring.
Use gentle cleansers and avoid irritation.
🧑⚕️ 2. Medical Treatment (Recommended)
For Lipomas:
Surgical removal: Done under local anesthesia. Best option for permanent removal.
Liposuction: Sometimes used if the lipoma is soft and fatty, but less common.
For Cysts:
Drainage: Doctor can drain the fluid, but cyst often returns without full removal.
Excision (removal): Minor surgery to remove the cyst wall and contents — most effective.
Injection (steroid): Reduces inflammation if cyst is inflamed but not infected.
🦠 3. Infected Cysts
Signs: Redness, swelling, pus, pain.
Treatment: May require antibiotics and incision and drainage by a doctor.
❓ When to See a Doctor
The lump is growing quickly
It’s painful, red, or leaking pus
It’s interfering with movement or appearance
You’re not sure if it’s a cyst or something else
✅ Summary
Lipomas: Benign fatty lumps → need surgical removal if bothersome.
Cysts: Can sometimes drain on their own, but usually need medical removal.
Avoid popping or squeezing.
See a dermatologist or general surgeon for proper diagnosis and treatment.
🧠 Lipomas
Definition: Lipomas are benign (non-cancerous) tumors composed of mature fat cells. They are typically soft, movable, and painless lumps that form just under the skin.
Characteristics:
Size: Usually small, but can grow larger over time.
Location: Commonly found on the shoulders, back, arms, and thighs.
Growth: Slow-growing and generally painless.
Treatment Options:
Surgical Excision:
The most effective method for complete removal.
Performed under local anesthesia.
Involves making an incision over the lipoma and removing it entirely.
Recurrence is rare if the entire lipoma is removed. Surgical Associates of Corpus Christi
Liposuction:
Involves using a needle and syringe to remove the fatty lump.
Less invasive but may not remove the entire lipoma, leading to potential recurrence. Mayo Clinic+2Wikipedia+2AAFP+2
Steroid Injections:
Can shrink the lipoma but may not eliminate it entirely.
Best suited for smaller lipomas.
When to Seek Medical Attention:
If the lipoma becomes painful, rapidly enlarges, or restricts movement.
If there’s uncertainty about the diagnosis, as some malignant tumors can mimic lipomas.
🧬 Sebaceous Cysts (Epidermoid Cysts)
Definition: Sebaceous cysts are benign, closed sacs under the skin filled with keratin. They often have a central pore and can appear on the face, neck, back, or genitals.Verywell Health
Characteristics:
Appearance: Small, round, and movable lumps beneath the skin.
Content: Filled with a thick, yellowish substance.
Symptoms: Usually painless but can become inflamed or infected.Verywell Health
Treatment Options:
Incision and Drainage:
A small cut is made to drain the cyst.
Provides temporary relief but doesn’t remove the cyst wall, leading to potential recurrence. Pristyn CareAAFP
Surgical Excision:
Involves removing the entire cyst, including the sac and contents.
Minimizes the chance of recurrence.
Best performed when the cyst is not inflamed. Wikipedia+1PMC+1
Minimal Excision Technique:
A tiny incision is made to remove the cyst contents and wall.
Leaves a smaller scar but may have a higher chance of recurrence if the entire sac isn’t removed.
When to Seek Medical Attention:
If the cyst becomes red, swollen, painful, or starts draining pus.
If there’s uncertainty about the diagnosis or if the cyst changes in appearance.
🖼️ Visual Comparison
Wikipedia+8Healthline+8Mayo Clinic+8
Note: The above image is for illustrative purposes. Please consult a healthcare professional for accurate diagnosis and treatment options.
📌 Summary
Lipomas: Benign fatty tumors that are usually painless and slow-growing. Surgical excision is the most effective treatment.
Sebaceous Cysts: Benign cysts filled with keratin. Treatment options include incision and drainage or surgical excision, depending on the situation.