Effective Blackhead Removal: Tips, Methods, and Prevention Blackheads are one of the most common skin concerns affecting people of all ages, especially those with oily or acne-prone skin. These tiny dark spots typically appear on the face, especially the nose, chin, and forehead, but can also occur on the back, chest, and shoulders. Understanding how to safely and effectively remove blackheads can lead to clearer, healthier skin. What Are Blackheads? Blackheads, also known as open comedones, form when hair follicles become clogged with oil (sebum), dead skin cells, and debris. Unlike whiteheads, which remain closed under the skin, blackheads have an open surface. When the trapped material is exposed to air, it oxidizes and turns black, giving blackheads their characteristic appearance. Causes of Blackheads Several factors contribute to blackhead formation: Excess oil production Hormonal changes (e.g., puberty, menstruation) Improper skincare Use of comedogenic (pore-clogging) products Environmental pollutants Blackhead Removal Methods Cleansing Use a gentle cleanser twice a day to remove dirt and oil.
Look for products containing salicylic acid or benzoyl peroxide, which help break down the materials clogging pores. Exfoliation Regular exfoliation removes dead skin cells and helps prevent clogged pores. Chemical exfoliants, like AHAs and BHAs, are often more effective and gentler than harsh scrubs. Pore Strips Pore strips can temporarily remove blackheads, especially on the nose. However, they don’t prevent new ones from forming and may irritate sensitive skin. Extraction Tools Comedone extractors can be used to manually remove blackheads. This should be done with caution and hygiene to prevent skin damage or infection. It’s often better left to professionals. Topical Treatments Retinoids (like adapalene or tretinoin) can increase cell turnover and help keep pores clear. These are especially useful for chronic blackhead issues. Professional Treatments Dermatologists and licensed estheticians offer treatments like facials, microdermabrasion, and chemical peels that can deeply cleanse pores and reduce blackheads effectively.
Tips for Prevention Keep Your Skin Clean: Always remove makeup before bed and wash your face after sweating. Use Non-Comedogenic Products: Choose skincare and cosmetics labeled as non-comedogenic. Don’t Over-Wash: Washing too often can strip skin of natural oils and trigger more oil production. Hydrate: Moisturize regularly to maintain skin balance, even if you have oily skin. Healthy Diet: A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and water can support clearer skin. Conclusion Blackhead removal doesn’t have to be a battle. With consistent care and the right techniques, you can minimize and manage blackheads effectively. If over-the-counter methods don’t work, consider seeing a dermatologist for personalized treatment. Remember, patience and a good skincare routine are key to clearer skin.
If you have big pimples on your forehead (sometimes painful, swollen, or cystic), here’s how to treat and manage them safely and effectively:
🚨 First: What Kind of Pimple Is It?
Forehead pimples can be:
| Type | Appearance | Treatment Approach |
|---|---|---|
| Papule | Red, inflamed bump | Anti-inflammatory topicals |
| Pustule | Has pus, yellow center | Spot treatments |
| Nodule/Cyst | Deep, painful, large lump | Needs medical treatment (don’t pop!) |
| Comedones | Blackheads/whiteheads | Exfoliation, cleansing |
✅ Step-by-Step Treatment: Big Forehead Pimples
1. Cleanse Gently
Use a gentle, non-comedogenic cleanser with salicylic acid (2%) or benzoyl peroxide (2.5–5%) to reduce oil and bacteria.
-
Example: CeraVe Acne Foaming Cleanser, La Roche-Posay Effaclar Gel
2. Apply Warm Compress
-
Use a clean, warm (not hot) compress for 10–15 minutes, 2–3 times a day.
-
This softens the skin and helps drainage if it’s coming to a head.
3. Spot Treatment (Over-the-Counter)
Apply:
-
Benzoyl peroxide gel (kills bacteria)
-
Salicylic acid (unclogs pores)
-
Sulfur-based treatments (dries excess oil)
-
Optional: Pimple patches (hydrocolloid) overnight to absorb pus and reduce size.
4. DO NOT Pop It
Especially for large or cystic pimples — popping can cause:
-
Infection
-
Scarring
-
Deeper inflammation
💊 Medical Treatment for Large or Cystic Forehead Pimples
If over-the-counter options don’t help in 1–2 weeks or the pimple is painful/deep:
1. Topical Prescription Treatments
-
Tretinoin (retinoid) – for clogged pores and cell turnover
-
Clindamycin – antibiotic gel/lotion
-
Azelaic acid – for redness + post-acne dark spots
2. Oral Medications
-
Antibiotics (e.g., doxycycline) – if inflamed or multiple lesions
-
Hormonal therapy (e.g., birth control, spironolactone for women)
-
Isotretinoin (Accutane) – for chronic, severe acne (requires close monitoring)
3. In-Clinic Procedures
-
Corticosteroid injection – reduces a large cyst within 24–48 hours
-
Manual extraction – by a trained professional
-
Chemical peels or microneedling – for acne and scarring
🔁 Prevention Tips (Especially for Forehead Acne)
-
Avoid heavy hair oils/products (pomade acne)
-
Wash face twice daily
-
Change pillowcases 2–3x per week
-
Avoid touching or rubbing forehead
-
Shampoo regularly if you have bangs or oily scalp
-
Use non-comedogenic makeup & sunscreen
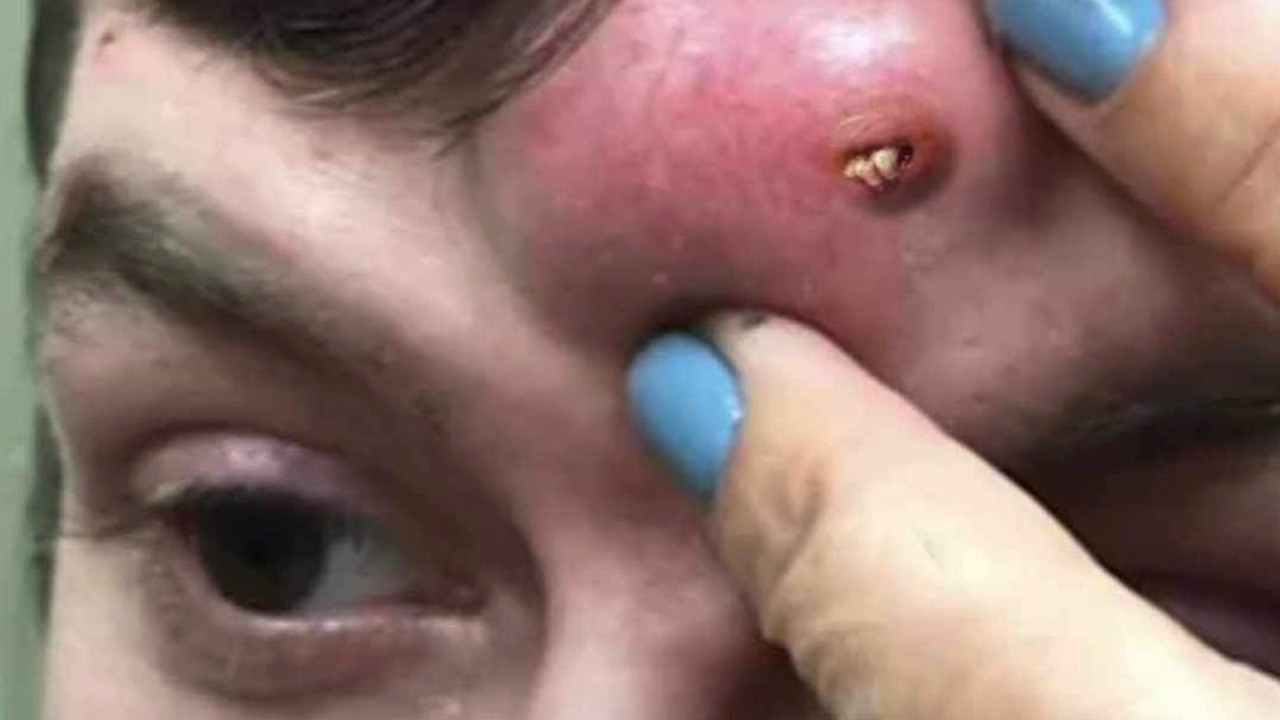
🧠 Understanding Large Forehead Pimples
Large pimples on the forehead, especially cystic acne, can be challenging to treat due to their depth and inflammation. These types of acne lesions often take longer than typical pimples to resolve and may not improve with standard skincare routines. Common causes include clogged pores, hormonal imbalances, certain medications, and improper skincare.
🧴 Effective Treatment Options
1. Topical Treatments
-
Benzoyl Peroxide: Kills acne-causing bacteria and reduces inflammation. Over-the-counter products with 5% or less are recommended to avoid dryness.
-
Salicylic Acid: A gentle exfoliator that unclogs pores, reduces oil, and clears blemishes. It’s suitable for sensitive skin and typically causes less irritation than benzoyl peroxide.
-
Topical Retinoids: Increase cell turnover, clear clogged pores, and reduce scarring. Start with a lower concentration (0.25%) and work your way up.
2. Professional Treatments
-
Corticosteroid Injections: Used to quickly shrink large, painful acne cysts.
-
Incision and Draining: Helps to open up an acne cyst and drain the pus.
-
Isotretinoin (Accutane): An oral retinoid for severe cystic acne that hasn’t responded to other treatments.
3. Home Remedies
-
Warm Compresses: Apply to the affected area for 10–15 minutes, 2–3 times a day, to reduce swelling and promote drainage.
-
Hydrocolloid Patches: These can help absorb impurities and reduce the size of the pimple.
🚫 What to Avoid
-
Popping Pimples: This can worsen inflammation, cause infections, and leave scars.
-
Over-Exfoliating: Excessive scrubbing can strip the skin of oil, leading to more oil production and potentially more acne. Limit exfoliation to once or twice a week.
-
Using Toothpaste: While a common home remedy, toothpaste can irritate the skin and worsen acne. Dermatologists advise against it.
🧼 Prevention Tips
-
Maintain Good Hygiene: Regularly wash your face and hair to remove excess oil and dirt.
-
Use Non-Comedogenic Products: Choose skincare and hair products labeled as non-comedogenic to prevent pore blockage.
-
Manage Stress: Practice relaxation techniques like yoga or meditation to reduce stress-induced breakouts.
-
Stay Hydrated and Eat a Balanced Diet: Proper hydration and a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins can support skin health.
🩺 When to Consult a Dermatologist
If a pimple persists for more than three weeks, is unusually large, or is causing significant discomfort, it’s advisable to consult a dermatologist. They can provide treatments such as cortisone injections or prescribe oral medications tailored to your condition.