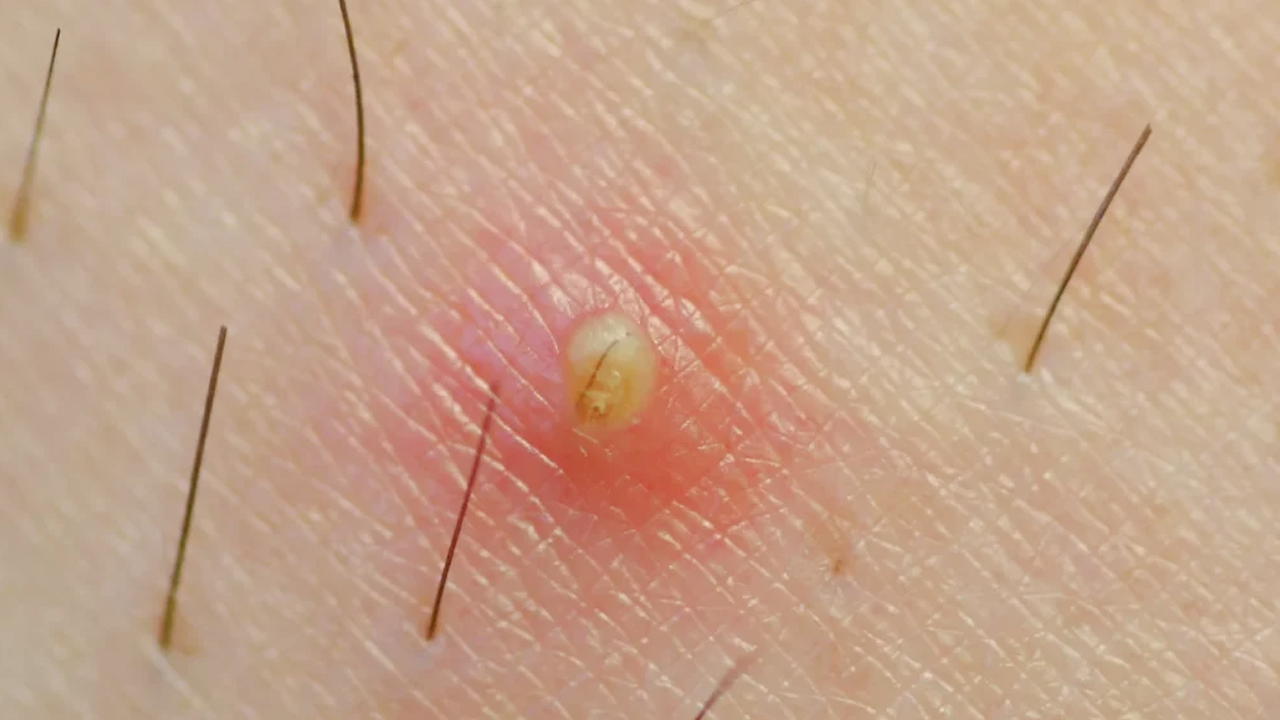
Removing a facial cyst should always be done with care to avoid infection, scarring, or complications. Here’s a clear breakdown of how it’s typically handled, either professionally or, in some cases, under careful home conditions. However, medical removal by a professional is strongly recommended.
✅ Medical (Professional) Cyst Removal
-
Evaluation: A dermatologist or doctor will assess the cyst to determine the type (e.g., sebaceous, epidermoid, pilar).
-
Anesthesia: The area is numbed with a local anesthetic.
-
Incision & Drainage or Excision:
-
For temporary relief, doctors may drain the cyst by making a small incision and squeezing out the contents.
-
For permanent removal, they may excise the entire cyst sac to prevent it from coming back.
-
-
Stitches: If a full excision is done, stitches may be needed to close the wound.
-
Aftercare: Antibiotic ointment is applied, and instructions for keeping the area clean are given. Follow-up may be scheduled.
⚠️ At-Home Approach (Not Recommended but Commonly Asked)
Only consider this for small, non-infected cysts and if you’re unable to access a doctor — even then, it’s risky.
-
Do NOT squeeze — this can push the cyst deeper and cause infection.
-
Warm Compresses: Apply a warm, damp cloth for 10–15 minutes, several times a day. This may help it drain naturally over time.
-
Tea Tree Oil or Iodine: Some use these for their antibacterial properties, but they won’t “remove” a cyst — just help prevent infection.
-
Keep Clean: Avoid touching or picking at it. Wash the area with gentle cleanser.
-
Watch for Signs of Infection: Redness, swelling, pus, pain, or heat may mean it’s infected and needs urgent medical attention.
❗When to See a Doctor
-
Rapid growth
-
Pain or redness
-
Leaking or bleeding
-
Returning cysts
-
Cosmetic concern or scarring risk
🩺 Medical (Professional) Cyst Removal
1. Diagnosis and Assessment
A healthcare professional will evaluate the cyst to determine its type (e.g., epidermoid, sebaceous) and decide on the appropriate treatment method.
2. Treatment Options
Incision and Drainage
-
Procedure: A small incision is made to drain the cyst’s contents.
-
Considerations: This method may not prevent recurrence if the cyst’s sac is not entirely removed.
Excision
-
Procedure: The entire cyst, including its sac, is surgically removed.
-
Benefits: Reduces the likelihood of recurrence.
Marsupialization
-
Procedure: A surgical technique where the cyst is opened and the edges are sutured to allow continuous drainage.
-
Indications: Often used for cysts that are difficult to excise completely .
3. Post-Procedure Care
-
Stitches: If excision is performed, stitches may be required.
-
Aftercare: Follow the healthcare provider’s instructions for wound care and hygiene to promote healing and prevent infection.
🏠 Home Care for Facial Cysts
While medical treatment is recommended, certain home care practices can alleviate symptoms:
1. Warm Compresses
-
Method: Apply a warm, damp washcloth to the cyst for 20–30 minutes, 3–4 times a day.
-
Purpose: Helps reduce inflammation and may encourage the cyst to drain naturally .
2. Avoid Squeezing or Popping
-
Reason: Attempting to drain the cyst manually can lead to infection, scarring, or deeper tissue damage .
3. Maintain Cleanliness
-
Action: Gently cleanse the area with mild soap and water to prevent infection.
4. Monitor for Infection
-
Signs: Increased redness, swelling, pain, or pus drainage may indicate infection, necessitating medical attention.
🌿 Natural Remedies (Adjunctive Use)
Some individuals explore natural remedies, though scientific evidence is limited:
-
Tea Tree Oil: Known for its antimicrobial properties, it may help reduce inflammation. Dilute before application to avoid skin irritation .
-
Turmeric: Contains anti-inflammatory compounds; can be consumed or applied topically in paste form.
-
Castor Oil: Believed to reduce cyst size and alleviate discomfort; apply sparingly to the affected area.
Note: Consult with a healthcare provider before using these remedies, especially if you have sensitive skin or underlying health conditions.
⚠️ When to Seek Medical Attention
Consult a healthcare professional if:
-
The cyst becomes painful, inflamed, or shows signs of infection.
-
The cyst grows rapidly or changes in appearance.
-
You have concerns about the cyst’s nature or potential complications.
For more detailed information on skin cysts and their management, you may refer to the following resources: