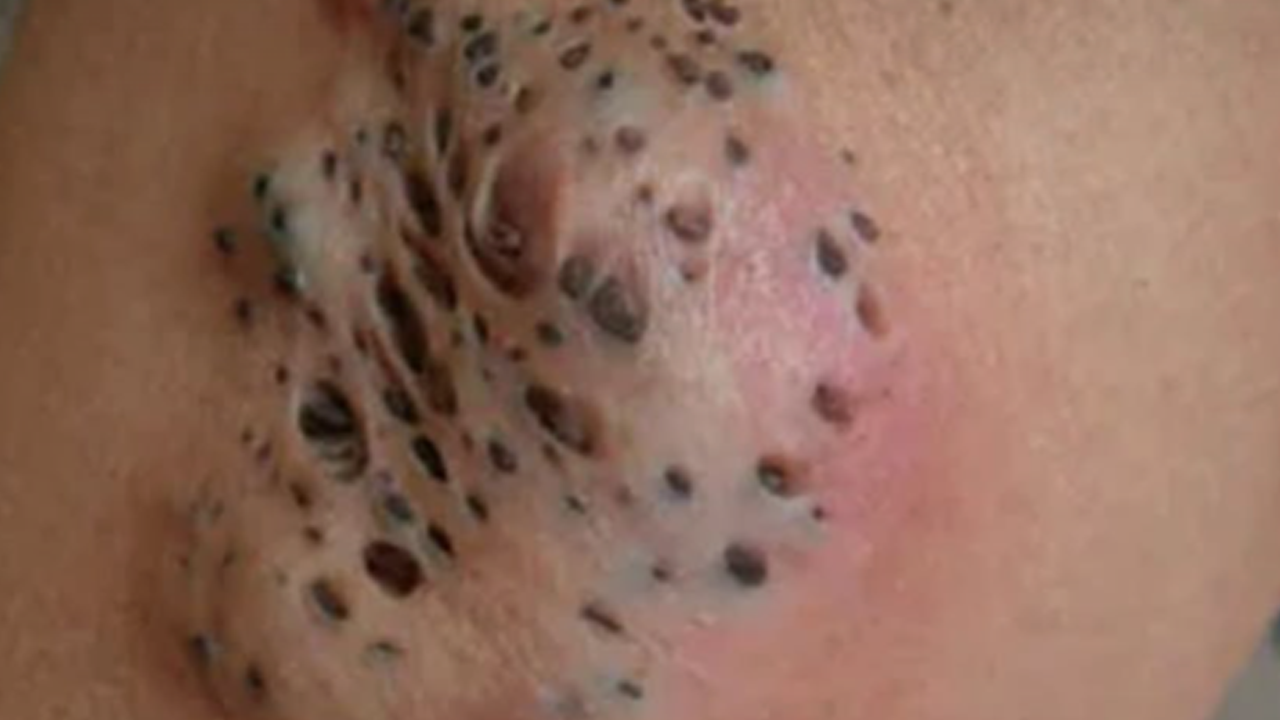
Nevus comedonicus (NC) is a rare, benign skin lesion characterized by clusters of dilated follicular openings filled with keratin (comedones), resembling blackheads. It’s often congenital or appears in childhood and may become inflamed or infected.
🧬 What Is Nevus Comedonicus?
-
A hamartomatous malformation of the pilosebaceous unit
-
Appears as grouped comedones in a linear or segmental distribution
-
May be non-inflammatory or develop secondary cysts, pustules, or abscesses
🧪 When Is Removal Indicated?
-
Cosmetic concerns
-
Recurrent infections or inflammation
-
Cyst or abscess formation
-
Pain or discharge
🛠️ Removal & Treatment Options
1. Topical & Medical Management (for mild cases)
| Treatment | Purpose | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Topical retinoids (e.g. tretinoin) | Unplug follicles, reduce comedones | May reduce appearance but won’t eliminate lesion |
| Antibiotics (topical or oral) | Reduce inflammation, treat secondary infection | For inflamed or infected lesions |
| Keratolytics (e.g. salicylic acid) | Break down keratin plugs | Temporary relief |
⚠️ These do not remove the nevus, only manage symptoms.
2. Surgical Removal (Definitive treatment)
A. Excision (preferred for localized NC)
-
Wide local excision of affected skin
-
Requires suturing or skin grafting if large
-
Pros: Permanent, complete removal
-
Cons: Scarring, anesthesia needed, cost
B. Laser Therapy
-
CO₂ laser or Er:YAG laser
-
Vaporizes superficial lesions
-
Best for: Multiple lesions or cosmetically sensitive areas
-
May require multiple sessions
-
Less invasive but recurrence possible
C. Punch Excision or Curettage
-
Used for smaller lesions
-
Minimally invasive
-
Can leave small scars
D. Dermabrasion or Chemical Peels
-
Sometimes used to reduce surface irregularities
-
Not curative for deep lesions
📋 Example Surgical Approach (for small NC lesion)
-
Local anesthesia
-
Full-thickness elliptical excision of affected area
-
Histological examination (to confirm diagnosis)
-
Closure with sutures
-
Follow-up to monitor healing and recurrence
📚 References
-
Lee M, et al. Nevus Comedonicus: Case Report and Review of Treatments. Dermatologic Surgery, 2015
-
NCBI: Nevus Comedonicus – StatPearls
-
Alikhan A, et al. Dermatology for the Primary Care Provider. (Elsevier, 2019)
🧴 Medical Management
Topical Treatments
-
Topical Retinoids: Tretinoin (0.1%) and tazarotene are commonly used to reduce comedones. Combining these with topical corticosteroids like mometasone furoate may enhance efficacy.
-
Topical Keratolytics: Salicylic acid and ammonium lactate (12%) can help in softening and removing keratin plugs.
-
Calcipotriene: A vitamin D analog that has shown promise when combined with other treatments.
Systemic Treatments
-
Oral Isotretinoin: Used in severe cases, especially when topical treatments are ineffective.
-
Antibiotics: May be prescribed if secondary infections occur.
🛠️ Surgical and Procedural Interventions
Surgical Excision
-
Indication: Recommended for large or disfiguring lesions.
-
Procedure: Involves complete removal of the affected skin.
-
Considerations: May require skin grafting or tissue expansion for closure.
Laser Therapies
-
Ultrapulse CO₂ Laser: Effective for deeper lesions; multiple sessions may be required.
-
Erbium-YAG Laser: Useful for superficial lesions; may require multiple sessions.
-
1450 nm Diode Laser: Targets sebaceous glands; may improve skin texture.
Other Procedures
-
Curettage and Dermabrasion: May be considered for smaller lesions.
🧩 Considerations
-
Diagnosis: Primarily clinical; biopsy may be performed to confirm.
-
Recurrence: Possible even after treatment; ongoing monitoring may be necessary.
-
Cosmetic Concerns: Treatment is often sought for aesthetic reasons, especially in visible areas.
📌 Conclusion
Nevus comedonicus is a benign condition with various treatment options tailored to the severity and location of the lesions. While medical treatments can offer symptomatic relief, surgical and laser interventions may provide more definitive solutions for disfiguring lesions. Consultation with a dermatologist is essential to determine the most appropriate treatment plan.